The Hyderbad Metro Rail

Traffic congestion is one of the most prevalent transport problems in large urban agglomerations, usually in metro cities. Transportation in Hyderabad is not an exception to this rule and also become major issue for the Government of Telangna. Keeping this in view, the Hyderabad Metro Rail (HMR) is being developed as one of the largest modern transport systems in the world based upon PPP (Public Private Partnership) model. The Government of India has in its futuristic reform document focused upon a strategy to promote fast- paced moving transport that would bring about equitable and sustainable improvements in the overall living standards of the citizens.
The denizens of Hyderabad are few months away to experience this metro rail transit system as HMR authorities are planning to conduct trial run between the two metro rail stretches of the two corridors by mid of October, 2017.The Hyderabad Metro rail Project is the world’s largest Public Private Partnership Project (PPP) in the metro sector. The project has a viability gap fund from Centre and State. Of the total cost, Government of India has sanctioned ten per cent as one time capital grant while remaining is being invested by the concessionaire L& T Metro Rail Hyderabad Ltd.
Based on number of surveys and studies conducted by various agencies, the then Government of Andhra Pradesh approved the project in three high density traffic corridors of the city spanning across 72 km (phase- 1). These three corridors are as under:
- Corridor 1: Miyapur –LB Nagar (29 kms, 27 stations)
- Corridor 2: JBS-Falaknuma (15 kms; 16 stations)
- Corridor 3: Nagole- Shilparamam; 28 Kms, 23 station
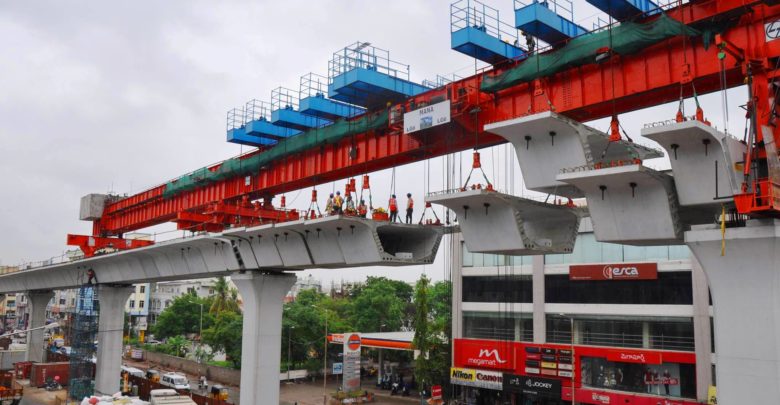
This prominent and largest metro project will have three elevated corridors interlacing the city of Hyderabad having metro stations en route in a distance of 1 km approximately. The viaduct structure for the elevated system is a box girder carrying two tracks on a single pier located on the median of the road. The metro rail network will pass through the principal roads of Hyderabad which connects major bus hubs, residential and commercial spots. The metro would be connected to currently running MMTS services and existing railway stations at various places in Hyderabad.
The trains have maximum designed speed of 90 km/ per hour and average speed of 33 km/ per hour and can run with headway of 3 minutes during peak and 15 minutes during lean hours with dwell time of 20 seconds per station to tackle commuters in morning and in evening. The rail coaches in Hyderabad metro are being supplied by Hyundai Rotem. The car body is made up of stainless steel/ aluminum. Trains will be air- conditioned throughout with designated space and have foolproof safety features and on- board fire & smoke detection as well. These trains will have longitudinal seat, grab poles and rails for standing passengers, CCTV cameras in and outside the cars, mobile and laptop charging sockets inside the car, better humidity control, microprocessor- controlled brakes, secondary air-suspension for better ride comfort. The train will be capable of maintaining an average speed of 33 km/ hour and maximum operating speed of 80 km/ hour.
The metro spanning over 72 kms in three of the densest corridors of the Hyderabad city will have total 66 stations with 3 stations being used as interchange stations. The balanced cantilever structural system (Spine & Wing) typically adopted for metro stations is a unique one. Entire structure will be resting on a single row of central columns located on the road median along the alignment. By virtue of this system there is adequate ventilation and lighting for road users below and there is no obstruction to the surrounding properties. The stations are being designed reflecting local culture and functional aesthetics. Stations are being covered by an overlapping roofing system, open at sides, covering the platform, staircases & escalators designed based on architectural elements and functional aspects. Hyderabad Metro focus is on people, ease and convenience for commuters and aesthetics. Eco friendly stations with natural ventilation, skywalks, ramps and host of commuter friendly facilities are at the heart of this project. Surroundings of the metro stations are being developed aesthetically with greenery, street furniture, etc.
The Hyderabad metro rail will be using several energy conservation measures such as use of regenerative electric breaking in the trains thereby converting the momentum into electrical energy and feeding back to power supply system while breaking. Having all salient features which will add to the comfort and safety of the commuter, it is aesthetics combined with comfort and safety. The advanced signaling & Train Control technology, Communication Based Train Control (CBTC), is adopted for this transit system to control the trains. Hyderabad Metro would be first in India to claim train control by CBTC technology. The trains running on three corridors will be controlled and monitored from state-of-the-art Operation Control Centre (OCC). Local ATS at station and VDU at interlocking station can also control the train when needed. Axle Counter based Fall-Back system is also adopted as secondary train detection system in all three corridors in unlikely event of failure of CBTC operation. The trains shall run on Automatic Train Operation (ATO) mode which is the normal mode of operation of trains. The Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system continuously monitors safe train operation and initiates necessary action if a train doesn’t perform as desired. All vital train borne equipment is highly safe and redundant to avoid any unwanted interruption of train service.
The three maintenance facilities (train depots) planned in 72 km rail network of Hyderabad Metro rail are located severally at Miyapur for corridor-1, Falaknuma for corridor-2 and Uppal for corridor-3. These maintain facilities are for stabling and maintenance of trains, rail systems and engineering maintenance vehicles. Each line has a supporting depot where all the trains of that line shall be stabled in night. These maintenance depots are manned round the clock and are equipped with all facilities and resources required for efficient and effective maintenance of rail system assets. Daily internal cleaning and proper inspection is carried out before inducting trains in service to provide safety, clean environment and ambience to passengers.
At present the engineers are concentrating on the execution of the project on stipulated time. The 1st phase of Hyderabad metro rail project set to be operational in November, 2107 while whole project set to be completed by next year. The metro is expected to cater to around 17 lakh people every day. This project upon completion will be a path breaker for introducing PPP mode in such kind of mega projects in near future.